|
P |
|
D |
|
D |
|
T |
T 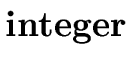 |
T 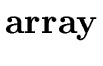 [ [ |
|
T |
|
T |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
We consider the language generated by the following grammar.
|
P |
|
D |
|
D |
|
T |
T 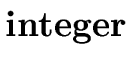 |
T 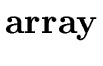 [ [ |
|
T |
|
T |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
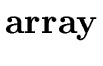 [
[| Grammar symbol | Synthesized attribute | Inherited attribute |
| E | E.type (type expression) | |
| T | T.type (type expression) | |
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
D |
{ addtype(id.entry, T.type) } |
|
T |
{ T.type :=
|
T 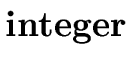 |
{ T.type :=
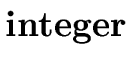 } } |
T 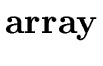 [ [ |
{ T.type := array
(0 ... |
|
T |
{ T.type := pointer(T1) } |
|
T |
{ T.type :=
(T1.type |
D  |
(1) |
|
E |
{ E.type := |
|
|
E |
{ E.type := |
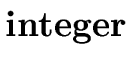 } } |
|
E |
{ E.type := | lookup(id.entry) } |
|
E |
{ E.type := | if
E1.type = 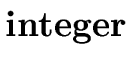 |
and
E2.type = 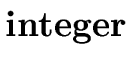 |
||
then
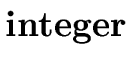 |
||
else
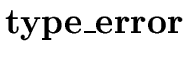 } } |
||
|
E |
{ E.type := | if
E1.type = 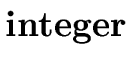 |
| and E2.type = array(n, T) | ||
| then T | ||
else
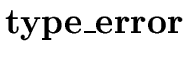 } } |
||
|
E |
{ E.type := | if E1.type = pointer(T) |
| then T | ||
else
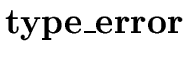 } } |
||
|
E |
{ E.type := | if E2.type = S |
| and
E1.type = S |
||
| then T | ||
else
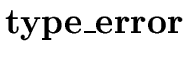 } } |
|
P |
|
D |
|
D |
|
T |
|
T |
T 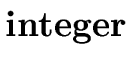 |
T 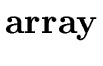 [ [ |
|
T |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
E |
|
S |
|
S |
|
S |
S 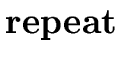 S S |
|
S |
{ S.type := | if S1.type = void |
| and S2.type = void | ||
| then void | ||
else
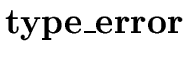 } } |
||
|
S |
{ S.type := | if E.type =
|
| then void | ||
else
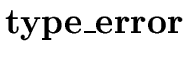 } } |
||
|
S |
{ S.type := | if E.type = boolean |
| then S1.type | ||
else
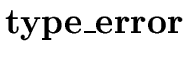 } } |
||
S 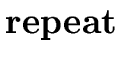 S1 S1 |
{ S.type := | if E.type = boolean |
| then S1.type | ||
else
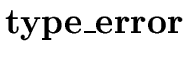 } } |